

Project of The Month
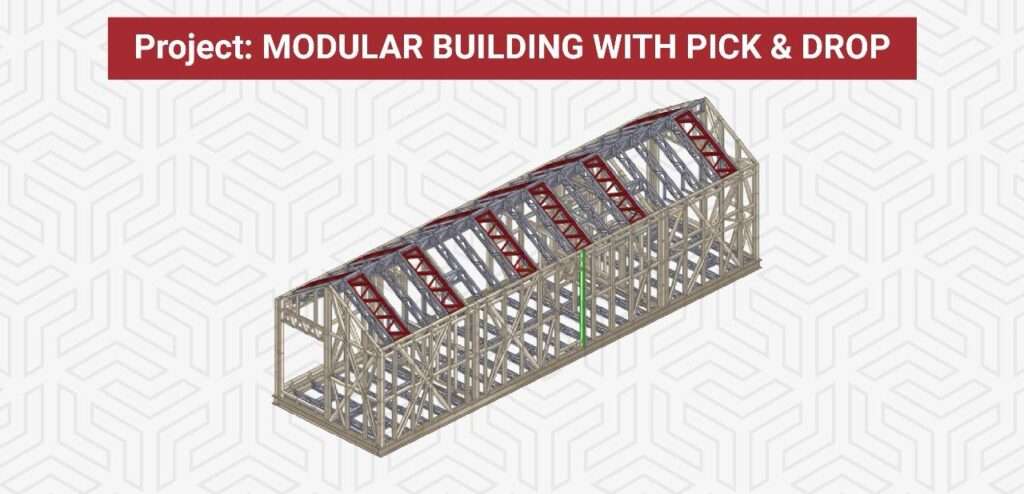
Project Type: MODULAR BUILDING WITH PICK & DROP
Area: 504 SFT
Roof : GABLE ROOF WITH SCISOOR TRUSSES
Scope of Work:
- ENGINEERING
- DETAILING
- CNC FILES
Software: Scotsteel
Machine: Scottsdale
Duration:10 days
Project Description:
This building is a 504 sq. ft. modular structure featuring a gable roof with scissor trusses, designed for durability and efficiency. Detailing done using Scotsteel and fabricated with a Scottsdale machine, the structure was carefully analyzed to withstand typical weather conditions, including heavy snow and strong winds. The superstructure is constructed using Light Gauge Steel Framing (LGSF), while the base is reinforced with Red Iron, ensuring both strength and stability. The project scope included engineering, detailing, and CNC file generation, all completed within a tight 10-day timeline.
A key feature of this modular building is its seamless transportation and installation process. The entire unit was prefabricated off-site and then lifted into place using hooks attached to the bottom of the Red Iron base. This pick-and-drop method not only streamlined logistics but also minimized on-site assembly time, enhancing efficiency. By combining LGSF and Red Iron, the structure achieves optimal load-bearing capacity while maintaining the flexibility needed for modular construction. This approach showcases UBC’s expertise in delivering high-quality, prefabricated buildings that meet both structural and operational requirements.

Steel and aluminum are ubiquitous in Americans’ lives. A stainless steel refrigerator holds aluminum soda cans. A stainless steel drum tumbles inside an aluminum washing machine. They’re the metals used in cars and airplanes, phones and frying pans, skyscrapers and zippers. Read more
Technical Snippet
The National Building Code of Canada (NBC) provides the framework for structural design and safety, ensuring buildings meet performance-based requirements for stability, durability, and occupant safety. It covers various aspects, including dead loads, live loads, snow loads, wind loads, and seismic forces, which are critical in designing Light Gauge Steel Framing (LGSF) structures.
The NBC is regularly updated, incorporating research, environmental considerations, and advancements in materials like cold-formed steel. Structural engineers designing with LGSF and hybrid materials like Red Iron must adhere to CSA S136, the standard for cold-formed steel design, ensuring compliance with limit states design (LSD) principles.
Load Calculations in LGSF Construction
Load calculations are fundamental to structural integrity, especially in harsh Canadian climates where snow and wind loads can be significant.
- Dead Load (DL):
- This includes the weight of structural components such as walls, floors, roofs, and permanent fixtures.
- Calculated based on material density and structural components.
- Live Load (LL):
- Considers occupant usage, furniture, and temporary loads.
- NBC mandates specific live load requirements for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Snow Load (S):
- Crucial in Canadian designs, especially in high-snow regions like Alberta, BC, and Ontario.
- Engineers use NBC maps and regional data to determine the correct snow load for modular or site-built structures.
- Wind Load (W):
- Calculated based on NBC wind maps, building height, exposure, and terrain.
- Includes gust effects and considers pressure coefficients.
- Essential for modular buildings, as they may experience additional wind loads during transportation and lifting.
- Seismic Load (E):
- Calculated using spectral response acceleration values.
- NBC mandates seismic design for zones prone to earthquakes, such as British Columbia.
- LGSF is advantageous in seismic design due to high strength-to-weight ratio and ductility.
Load Combinations As Per Canadian Code:

Engineering analysis using these combinations is performed under heavy snow conditions. The critical point is maintaining a high factor of safety compared to other codes.
Application in Prefabricated & Modular Buildings
In modular construction, load calculations must consider transportation and lifting load. Buildings lifted by hooks (as in Red Iron base-supported structures) must account for dynamic forces during hoisting and placement. Engineers ensure stability by distributing loads efficiently and reinforcing connection points.
By following NBC guidelines and advanced structural analysis tools, UBC ensures that its LGSF and hybrid buildings meet stringent Canadian code requirements, offering safe, efficient, and long-lasting structures.

